[Edit of 16/11/2018] We have updated the comparative table of nutri-scores of the bars to add information about Our bar.
For a few days, our vitaline bottles proudly have the Nutri-score logo with the big green letter "A"! 😀 🎉
We decided to set up the Nutri-score for reasons of transparency, and because we find it a very good initiative: inform consumers about the nutritional quality of the products they buy and guide them in their choices To eat better and be healthy.
Even if this indicator has certain limits (we talk about it below), its implementation is already a big step forward!
- The Nutri-Score, what is it?
- The Nutri-score of Vitaline is in the top of the European market, and the best on the French market
- The strengths and limits of the Nutri-score
- Vitaline with 5 criteria more pointed
- To go further: Scan your bottles on Yuka!
The Nutri-Score, what is it?
The Nutri-score measures the nutritional quality of a product by positioning it on a scale of A (in green = the best nutritionally) to E (in red = the least nutritionally good).

And guess what? Vitaline gets the letter A on the entire range! 👏
This indicator has been developed by Public Health France following the work done by the teacher Serge HERCBERG (Chairman of the National Nutrition Health Program and Director of the Nutrition Epidemiology Research Unit), theHandles (National Agency for Sanitary Safety of Food, Environment and Labor) and the High Public Health Council1.
The nutri-score calculation takes into account the nutritional elements to promote and limit. It takes into account for 100 g or 100 ml of product:
- The "Negative" component N: The energy content (KJ), saturated fatty acids (G), in simple sugars (G) and sodium (mg). The sum of these elements is between 0 and 40.
- The "Positive" component P: The protein content (G), fruit, vegetables, legumes and nuts (G or%) and fiber content (G). The sum of these elements is between 0 and 15.
The overall score of a food is obtained via this calculation:
Global Score = Σ (Items N) - Σ (P)2
It is between -15 (the most nutritionally favorable) and +40 (the most unfavorable). The score obtained allows to assign a letter and a color to the product, as specified in the table below3 :
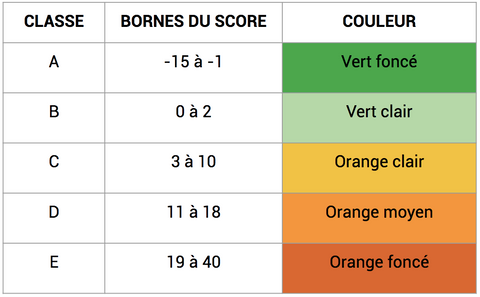
If you want to calculate the Nutri-score of a product yourself, here is the calculation table. Simply download or duplicate the document to reuse it.
To learn more about the Nutri-Score, go to the website of the National Nutrition Health Program.
The Nutri-score of Vitaline is in the top of the European market, and the best on the French market 🏆
We calculated the Nutri-score of seven European drinking comprehensive meal brands to compare them. Almost all brands get the letter A, but there are differences in quality by looking at the scores closer. Four brands stand out from the pack thanks to better notes (-4 and -3): Ambronite, Huel, Jimmy Joy and Vitaline 😀
All data and method of calculation are available in This complete comparative(drinking meal and bars).
Comparative Nutri-scores of European drinking meals
| Vitaline | Score | Letter |
|---|---|---|
| Vitaline tomato vegan | -3 | AT |
| Vitaline Carrot Curcuma | -2 | AT |
| Vitaline red fruits | -3 | AT |
| Vitaline cocoa | -3 | AT |
| Vitaline Almond | -3 | AT |
| Vitaline Ignite (pre-sport) | -1 | AT |
| Vitaline Recover (after-sport) | -3 | AT |
| Brand | Score | Letter |
|---|---|---|
| Ambronite (SW) | ||
| Ambronite original | -3 | AT |
| Feed (en) | ||
| Feed Ceps - Bottle | 0 | B |
| Garden Vegetables Feed - Bottle | 0 | B |
| Feed Carrot Pumpkin - Bottle | 1 | B |
| Feed Tomatoes at the Provençale - Bottle | 1 | B |
| FEED Chocolate - Bottle | 0 | B |
| Red Fruit Feed - Bottle | 0 | B |
| Bio Feed Olives Tomatoes - Bottle | 0 | B |
| BIO FEED FEED BASILIC - Bottle | 0 | B |
| Huel (UK) | ||
| Huel Vanilla v2.3 | -4 | AT |
| Jake (NL) | ||
| Jake Oaty Vanilla | -2 | AT |
| Jimmy Joy (NL) | ||
| JimmyJoy Penny Shake Vanilla | -3 | AT |
| QUAL (NL) | ||
| STANDARD QUAL | -2 | AT |
| QUAL VEGAN | -2 | AT |
COMPARATIVE OF NUTRI-SCORES OF THE EUROPEAN BARS
We also interested in products as a bar proposed on the market.4
| Brand | Score | Letter |
|---|---|---|
| Vitaline (FR) | ||
| Vitaline Carrot Bar - Sweet Potato | -1 | AT |
| Feed (en) | ||
| Feed bar red fruits | 7 | VS |
| Feed bar chocolate bar | 7 | VS |
| FEED Bar Bio Cranberries Chocolate | 10 | D |
| Feed bar organic figs almond | 0 | B |
| Huel (UK) | ||
| Huel Bar Cocoa | 7 | VS |
| Jake (NL) | ||
| Jake Vitamin Bar Coffee Cocoa | 8 | VS |
| Jimmy Joy (NL) | ||
| Jimmyjoy Twenny Bar Vanilla | 8 | VS |
| QUAL (NL) | ||
| QUAL CHOCOLATE BAR | 8 | VS |
Vitaline products get good scores because they have good protein and fiber contents, and little salt, sugar and saturated fatty acids.
The products of our category that have the lowest scores are generally penalized by too large salt and sugar contents. For example :
- Sugar contents:
- Vitaline Daily range (cocoa, almond, red fruit, carrot-curcuma, tomato): between 1.7 g and 2 g per 100 ml.
- Feed (cep bottle, garden, tomato, carrot pumpkin, red fruits, chocolate): between 4.3 g and 5 g of sugar for 100 ml.
- Sodium contents:
- Vitaline Daily range: between 62 mg and 89 mg sodium per 100 ml.
- Feed bottle tomatoes in the Provençale (160 mg of sodium), feed bottle vegetables from the garden (160 mg of sodium), Jake Oat Vanilla (98 mg of sodium) per 100 ml.
Nutri-score is not built to evaluate pre-sport foods. It is therefore normal that vitaline Ignite gets a less good score that other vitalines: it contains fewer proteins, less fiber and more sodium5. Nevertheless, it is in category A because its nutritional values remain excellent.
The strengths and limits of the Nutri-score
The method of calculating the Nutri-score is based on nutritional criteria that are consensus within the scientific community, it is its great strength:
- Protein, fiber, nuts, fruits and vegetables is valued;
- Lipids are not "diabolized" because saturated fatty acids are well distinguished from lipids in general. Excessive consumption of saturated fatty acids is harmful, unlike unsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids, hence the importance of separating fatty acid types;
- The sugars content is taken into account6 ;
- The salt content is taken into account7 ;
The Nutri-Score, however, has its limits and does not encompass all dimensions. To go further in the level of sophistication of the measurement of nutrition quality, we could add 5 criteria taking into account:
- Additives : Additives encompass a whole family of ingredients. Some additives are safe (like those contained in vitaline), but some can be toxic when they are eaten too much8.
- Diversity of lipid sources : The more varied the lipid sources, the lower the fatty acid profile balanced, and therefore beneficial for health.
- Omega 6 / Omega 3 ratio: plus the omega 6 / omega 3 ratio is low, the better.
- Nutritional qualities used oils : Oils do not have the same nutritional quality. For example, they are of better quality when they are virgin and organic.
- Protein qualitywhich depends in particular on the source of protein thus of their aminogram (the amino acid profile) and their digestibility (anti-nutritional factors). The amino acids do not have the same functions, various sources have very different and sometimes very unbalanced profiles, it is a significant simplification that not to consider the equilibrium of the profile.
- The origin of the products and their certifications.
-
The raw fruit and vegetable content (not dehydrated): Today the Nutri-score is based on a calculation grid by weight of ingredients. However, there is a big deformation with dehydration, mainly for fruits and vegetables that are composed between 75% and 95% water.
To illustrate, the buckwheat is not dehydrated in Vitaline, it is already dry: so 100 g of buckwheat in a classic food = 100 g in vitaline.
But tomatoes lose about 95% of their weight: 100 g "raw" tomatoes give 10 g in Vitaline (before rehydration).
If we take the vitaline tomato example, we have 20.4 g of vegetables for 100 g of vitaline. However, if these products were taken before dehydration, 60.18% of fruits and vegetables are obtained in proportion. The table below makes it possible to better understand the idea:
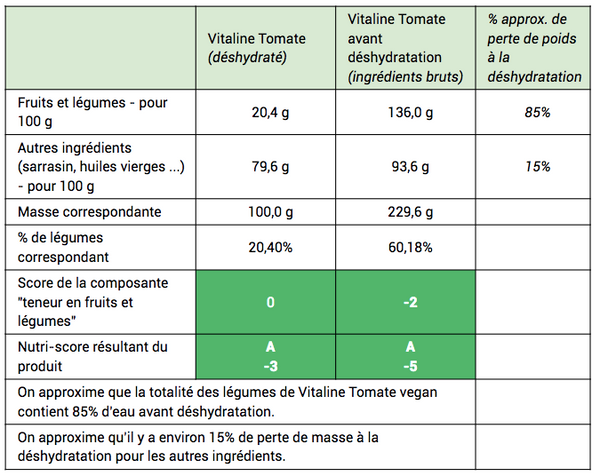
If you want to deepen the subject, we advise you reading this article: "The Nutri-Score measures the nutritional quality of food, and it's already a lot". It was written by a nutritionist doctor and two nutrition researchers, including Professor Serge Herchaberg, who defended the establishment of the Nutri-Score.
Vitaline with 5 criteria more pointed
To complete the measure of the Nutri-score and go to the end of our reasoning, we evaluated Vitaline on the 5 criteria cited above:
- Presence of additives :
- Vitaline contains only the organic rosemary natural extract (which protects the oxidation oils) and for some recipes, natural aromas, counted as additives.
- Huel Vanilla v2.3 has a very good score (-4) but contains two thickeners (xanthan and guar gum) and a sweetener (sucralose). Sucralose is an authorized additive, but is suspected of decreasing the variety of bacteria contained in the intestinal microbiota9.
- JimmyJoy Penny Shake Vanilla has a good score (-3) but contains two additives (Guar and sucralose gum).
- Fatty acid profile
- Omega 6 / Omega 3 ratio : Vitaline has an omega 6 / omega ratio between 1.1 and 2.7, but we advise a ratio of less than 4, knowing that the average diet of Westerners has a ratio of 1710. To obtain a good ratio, we use oils having a very good content in omega 3. Conversely, some products contain mainly sunflower oil, which has less nutritional qualities with an omega 6 / omega 3 ratio. close to 1000.
- Quality of oils : We use virgin and organic oils (rapeseed, oleic sunflower and linen) in Vitaline tomato vegan.
- Quality of proteins
- All vitaline recipes combine several sources of protein: organic pea proteins and organic sunflower proteins for Vitaline Vegan tomato for example. This type of protein combination provides a complete essential amino acid profile.
- Origin of ingredients and certifications
- In our tomato vegan version, 94% of the ingredients come from organic farming, and we have an average of 85% organic ingredients on all of our products.
- Gross fruit and vegetable contents
- Vitaline has the highest fruit and vegetable levels among the brands cited in our study (see Complete comparison).
- For example, Vitaline Tomato Vegan contains 20.4% fruit and vegetables for 100 g (before rehydration), and feed bottle tomatoes at the Provençale contains 7% per 100 g.
To go further: Scan your vitaline bottles on Yuka!
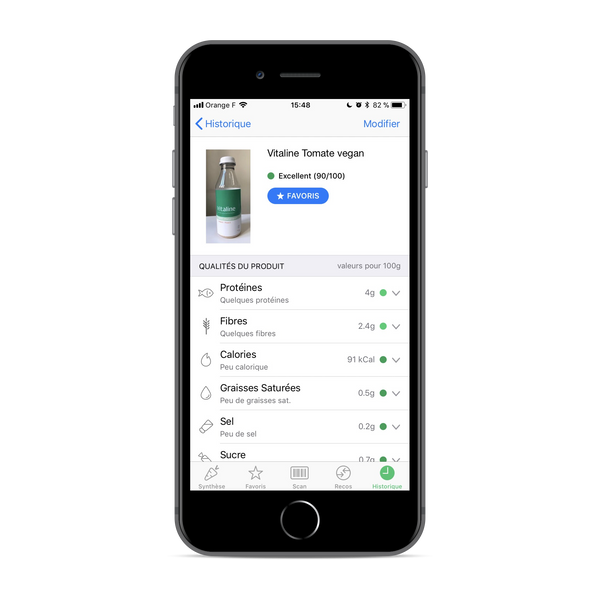
We are now present on the application Yuka who "scans your food". The application is based on the Nutri-score and adds other criteria, such as the presence of additives and their harmfulness for example.
Our products are not all listed yet because Yuka needs a barcode, and our new labels have since July 2018. Our versions are being referenced 😄
On Yuka, our VEGAN tomato version gets The excellent score of 90/100 ! 💪😎 And it is not finished, the only criterion that prevents us from having 100/100 is the organic label, which we should get in September 🚀 !
References :







